The Gestalt theory of logo design is a concept rooted in the field of psychology and design, emphasizing the idea that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. It provides a framework for understanding how humans perceive and make sense of visual elements and how this understanding can be applied to logo design. The Gestalt theory is a fundamental principle that designers often rely on to create effective and memorable logos.
Key principles of the Gestalt theory in logo design include:
- Proximity: This principle states that objects placed close to each other are perceived as a group or related, while objects spaced farther apart are seen as separate. In logo design, grouping elements that share a visual relationship can convey unity and a clear message.
- Similarity: When elements share common attributes, such as shape, color, or size, they are perceived as belonging together. A logo may use this principle by ensuring that related elements share these common features, reinforcing a sense of cohesion and identity.
- Continuation: This principle suggests that elements arranged in a continuous line or pattern are perceived as related or part of a sequence. Designers can use continuation to guide the viewer’s eye and create a sense of flow within a logo.
- Closure: Closure is the idea that the human mind tends to complete incomplete shapes or patterns. In logo design, partial elements or hidden shapes can engage the viewer’s imagination, making the logo more memorable and intriguing.
- Figure-Ground: This principle relates to the perception of an object (the figure) against its background (the ground). A well-designed logo should have a clear distinction between the main message (figure) and the background to ensure clarity and visibility.
- Symmetry and Balance: The Gestalt theory also highlights the human preference for symmetry and balance. Logos that are visually balanced and symmetrical often appear more pleasing and harmonious to the eye.
By applying these principles, logo designers can create logos that are visually appealing, easily recognizable, and able to convey a brand’s identity or message effectively. Here are some examples of famous logos that incorporate the Gestalt principles:
- The Apple logo: The apple with a bite taken out of it is a simple and memorable design. The bitten area provides closure and intrigue, and the overall shape is highly symmetrical.
- FedEx: The hidden arrow between the “E” and the “x” in the FedEx logo uses the principle of closure and cleverly reinforces the idea of forward movement.
- IBM: The IBM logo uses horizontal lines and a well-balanced design, adhering to the principle of symmetry and balance.
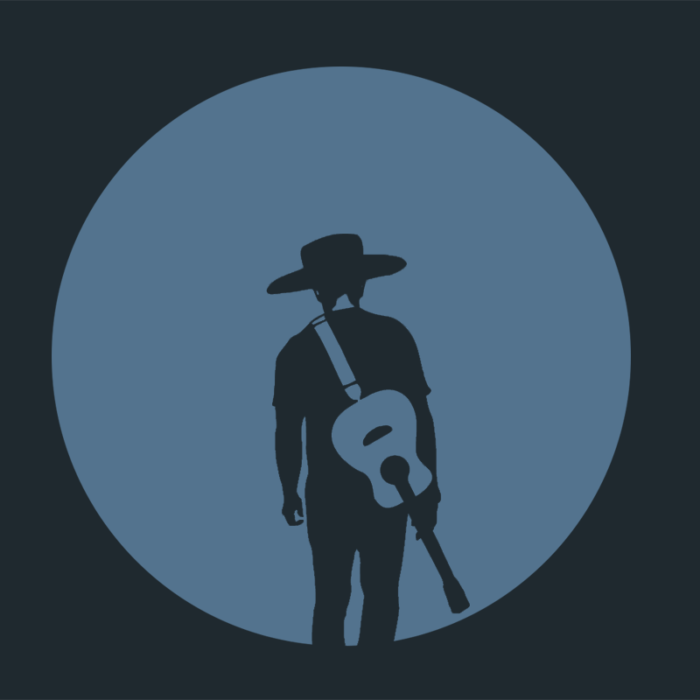
I don’t consider myself a designer, but I have taken classes and dabbled in design for school, work and personal projects. These samples are a couple elements I crafted for two websites I’ve been working on – Arnoldhaven.com – a site promoting my Short Term Rental and Ramblingmedia.com – my production company brand I’ve created.
The rambling media logo was inspired by a rambling traveler like my Great Uncle and one of his favorite songs “Rambling Man” by the Allman Brothers .
Brand development is the process of strategically creating and shaping a brand’s identity to establish a unique and compelling presence in the market. It involves defining the brand’s personality, values, and promise to customers, and then expressing these aspects through various brand elements.
- Brand Identity: Brand identity encompasses the visual and verbal elements that represent the brand. This includes the brand name, logo, color palette, typography, and tagline. These elements should be designed to convey the brand’s personality, values, and differentiation from competitors.
- Brand Voice and Messaging: A consistent and compelling brand voice is essential for conveying the brand’s personality and values. Messaging should be crafted to resonate with the target audience and reflect the brand’s unique selling points.
- Brand Guidelines: Establishing brand guidelines is crucial to maintain consistency across all brand touchpoints. These guidelines define how the brand elements should be used and ensure a uniform brand experience.